Laravel for beginners can feel overwhelming at first, but with the right guidance, it becomes a powerful and enjoyable PHP framework to learn. Known for its elegant syntax and developer-friendly features, Laravel makes it easier to build scalable, secure web applications.
👉 If you haven’t set up Laravel yet, check out our step-by-step guide on how to install Laravel framework 12.x on Windows.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through the basics — from understanding the MVC architecture to exploring important files like .env, routes, models, views, and controllers.
Table of Contents
What is Laravel?
Laravel is a great choice for beginners looking to build modern web applications quickly. This makes it ideal for anyone searching for practical tutorials on Laravel for beginners.
Laravel is a PHP web application framework with expressive, elegant syntax. It follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern, making it easier to separate your logic, UI, and data.
Whether you’re building a blog, a web app, or an e-commerce platform, Laravel gives you the tools and structure to do it faster and better.
Understanding MVC Architecture
One of Laravel’s core strengths is its support for the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern. Let’s break down what each part does:
- Model: Handles the data and business logic. It interacts with the database.
- View: The UI or frontend that users interact with.
- Controller: Connects the Model and View, processes input, and returns responses.
By separating these concerns, Laravel promotes cleaner code and easier maintenance.
Example Flow:
- A user visits
/posts. - Laravel routes the request to
PostController@index. PostControllerfetches posts from thePostmodel.- The controller passes data to the
index.blade.phpview. - The view displays the posts to the user.
Understanding MVC is a core concept in Laravel for beginners, as it helps you organize your application logic and presentation cleanly.
Key Files and Directories in Laravel You Should Know
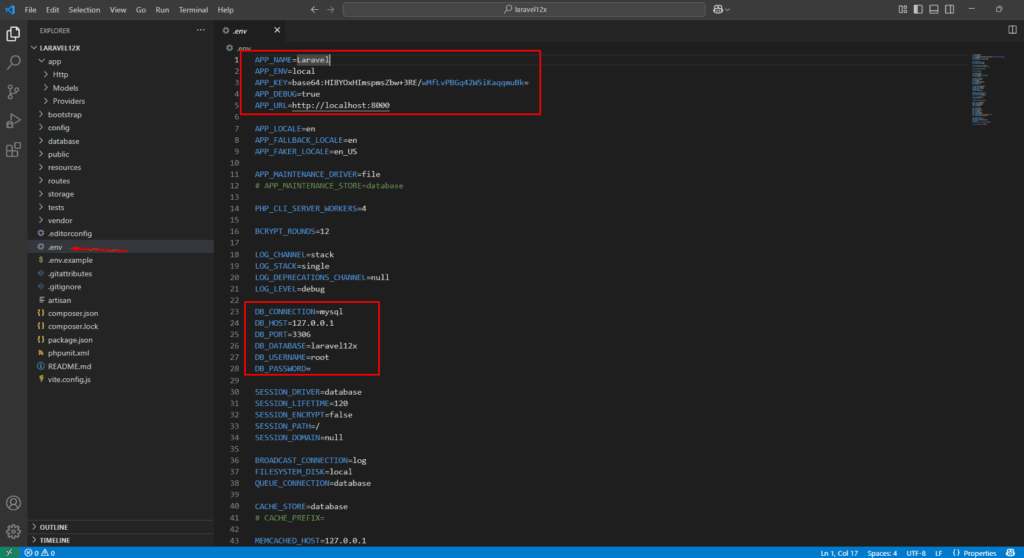
.env – Environment Configuration
Located in the root directory, the .env file stores environment-specific variables such as database credentials, app name, and debug mode.
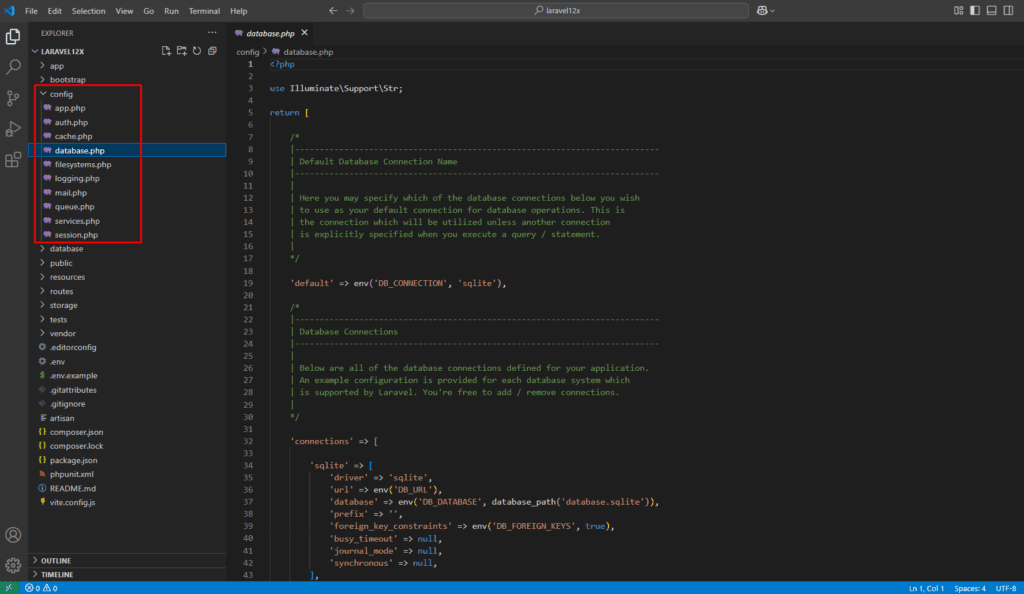
config/ – Application Configuration
This directory contains multiple files like app.php, database.php, and mail.php where you can configure various parts of your application.
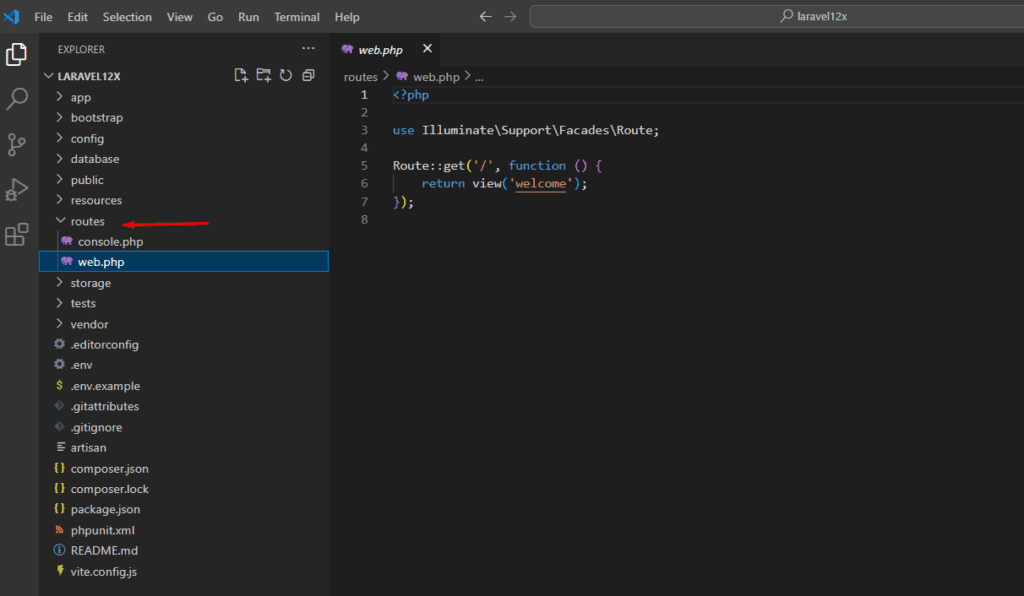
routes/web.php – Web Routes
This file defines all your web routes. You can define URL paths and map them to specific controller methods or closure functions.
app/Models/ – Models
Models define the structure of your application’s data and typically represent a table in your database. For anyone learning Laravel for beginners, understanding how models work is a key step in building database-driven applications. Laravel uses a clear and consistent naming convention that keeps your code clean and organized. Following these conventions when creating models and their related tables helps ensure everything works seamlessly with Laravel’s built-in features.
By default, Laravel expects your database tables to include some common columns:
id: The primary key (usually auto-incrementing).created_at: Timestamp for when a record was created.updated_at: Timestamp for when a record was last updated.deleted_at: Used for soft deletes (when enabled).
Laravel automatically manages created_at and updated_at, and if you enable soft deletes, it will also handle deleted_at. Including these columns lets you take full advantage of Laravel’s powerful Eloquent ORM.
✅ Model Naming
Model class names in Laravel should be singular and use PascalCase (also known as StudlyCase), where each word starts with a capital letter and there are no underscores.
Examples:
- If your table name is
products, the model class name should beProduct. - If your table name is
product_categories, the model class name should beProductCategory.
Laravel automatically maps the singular model name to its corresponding plural table name using its naming conventions. Following this rule keeps your code clean and compatible with Eloquent ORM.
✅ Table Naming
By default, Laravel assumes that the table name is the plural, snake_case form of your singular, PascalCase model name.
Examples:
- If your model class is
Product, Laravel expects the table name to beproducts. - If your model class is
ProductCategory, the corresponding table name should beproduct_categories.
This convention allows Laravel’s Eloquent ORM to automatically link models to their respective tables without needing to manually define the table name.
✅ Relationship Naming Conventions
When defining relationships between models, such as one-to-one or one-to-many, Laravel follows a naming pattern that’s important to learn — especially for Laravel for beginners.
📌 Table Column Naming Rules:
- Use singular snake_case for the foreign key column.
- The foreign key column should be named after the related model name followed by
_id.
Let’s say we have two tables: products and product_categories. Each product belongs to a product category. In this case, the products table should include a foreign key that points to the product_categories table.
According to Laravel’s naming convention, the foreign key column in the products table should be named:
product_category_idThis tells Laravel that the products table is related to the product_categories table through that column. Following this naming pattern helps Laravel automatically handle the relationship when using Eloquent.
📌 Relationship Method Naming:
In the model, use camelCase for relationship methods. And to create a model file, you can either manually add it using your code editor or use Laravel’s built-in Artisan command for faster and cleaner generation.
- A
Productmodel:
php artisan make:model Product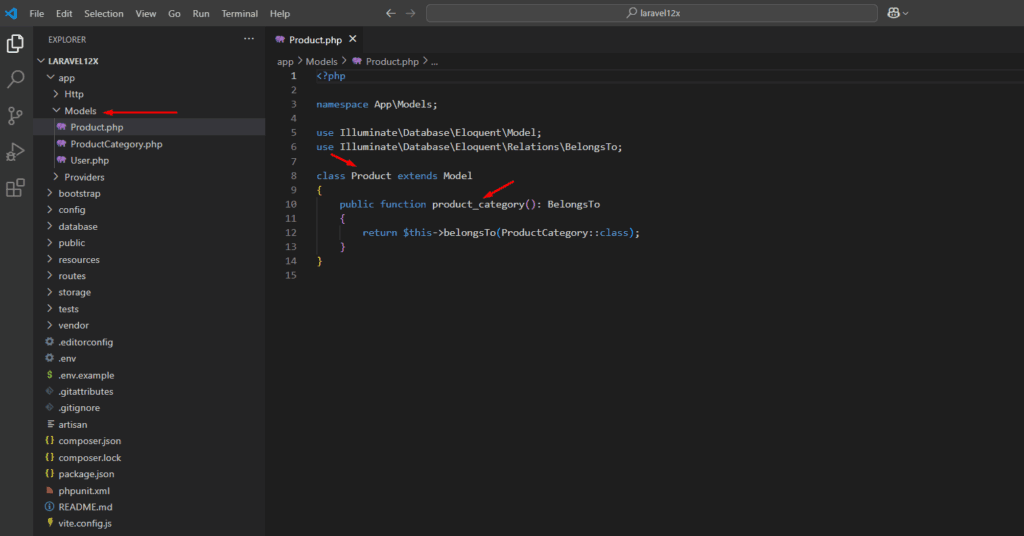
- A
ProductCategory model:
php artisan make:model ProductCategory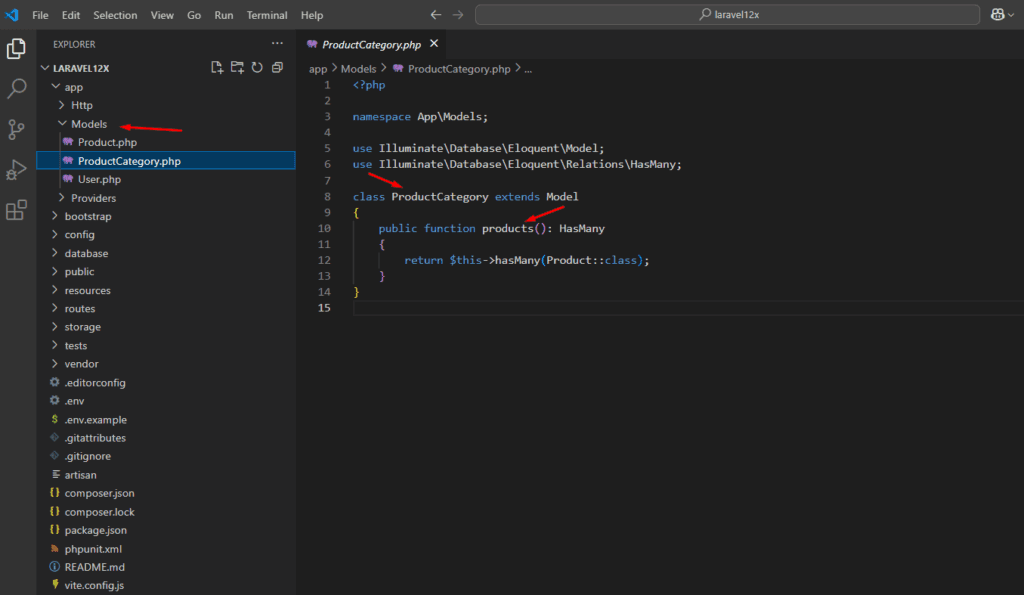
Following these conventions is essential for writing clean, error-free code in Laravel — especially when you’re just getting started with Laravel for beginners.
🔁 Custom Table Name (If Needed)
If your table name doesn’t follow Laravel’s default pattern, you can manually define it in your model:
Laravel uses this convention to automatically map the model to the correct table using Eloquent ORM. You don’t need to manually define the table name unless it differs from the convention.
class CustomModel extends Model
{
protected $table = 'my_custom_table';
}✅ Tip: Always follow Laravel’s naming conventions unless you have a specific reason not to. It saves time and reduces configuration.
resources/views/ – Blade Templates
Laravel uses the Blade templating engine for its views. These are the files where you write your HTML and embed dynamic content. To create a view file, you can either manually add it using your code editor or use Laravel’s built-in Artisan command for faster and cleaner generation.
php artisan make:view product/index
app/Http/Controllers/ – Controllers
Controllers contain the logic for handling incoming requests and returning responses. To create a controller file, you can either manually add it using your code editor or use Laravel’s built-in Artisan command for faster and cleaner generation.
php artisan make:controller ProductController
These files are essential in any Laravel project, and understanding them is a must for anyone learning Laravel for beginners.
Laravel for Beginners: Quick Tips
- Use Artisan Commands: Laravel includes a CLI called Artisan for tasks like creating controllers, models, and migrations.
- Stick to Conventions: Laravel follows naming and directory conventions. Following these will make your project cleaner and easier to maintain.
- Learn Eloquent: Eloquent is Laravel’s ORM. It helps you interact with the database using object-oriented syntax.
- Read the Docs: The official Laravel documentation is very beginner-friendly.
Final Thoughts
Learning Laravel as a beginner might seem overwhelming at first, but with a solid understanding of MVC and the key files in a Laravel project, you’ll be off to a great start. Focus on building small projects, exploring the file structure, and using Artisan commands to speed up your development.
If you’re just getting started, keep experimenting with small projects and exploring the documentation. With practice, Laravel for beginners becomes less intimidating and more enjoyable.
Don’t forget to bookmark this Laravel beginner’s guide and come back whenever you need a quick refresher.